Summary
The ERP Implementation Life Cycle is a structured process that guides organizations from planning to post-go-live support. It includes key stages like system selection, process mapping, data migration, testing, training, and deployment. Each phase builds on the previous one to ensure smooth adoption and long-term efficiency. Proper execution minimizes risks, improves team coordination, and maximizes ROI. Ignoring any stage can lead to errors, delays, or cost overruns. A well-managed ERP life cycle is essential for business success.
Introduction
ERP software is the backbone of business management. It helps to unify different processes into one system. However, it is important to deploy the solution properly, which requires structure, strategy, and patience. The ERP Implementation Life Cycle helps with all this. It guides organizations through every stage. All the phases in the life cycle play an important role in ensuring that your ERP project delivers value. In this article, you will go through all the stages of the life cycle in detail.
Something About ERP Implementation Life Cycle
It refers to the step-by-step process to deploy the ERP software within an organization. It starts with the planning process and ends with proper deployment with ongoing support. The goal is to achieve successful adoption and long-term efficiency for your business.
This life cycle includes:
- Understanding business needs
- Choosing the right system
- Mapping processes
- Data migration
- Testing
- Training
- Going live
- Post-go-live optimization
Each step builds upon the last. Missing one could lead to errors, resistance, or cost overruns.
Why Is It Important?
ERP systems touch every part of your business. All the elements are connected, like:
- Finance
- HR
- Inventory
- Customer service, etc.
This integration boosts visibility and productivity. However, it only works if the implementation is well-managed.
The life cycle provides a framework. It reduces risks. It improves communication across teams. It keeps projects on time and within budget. Most importantly, it helps organizations get full value from their ERP investment.
Stages of The ERP Implementation Life Cycle
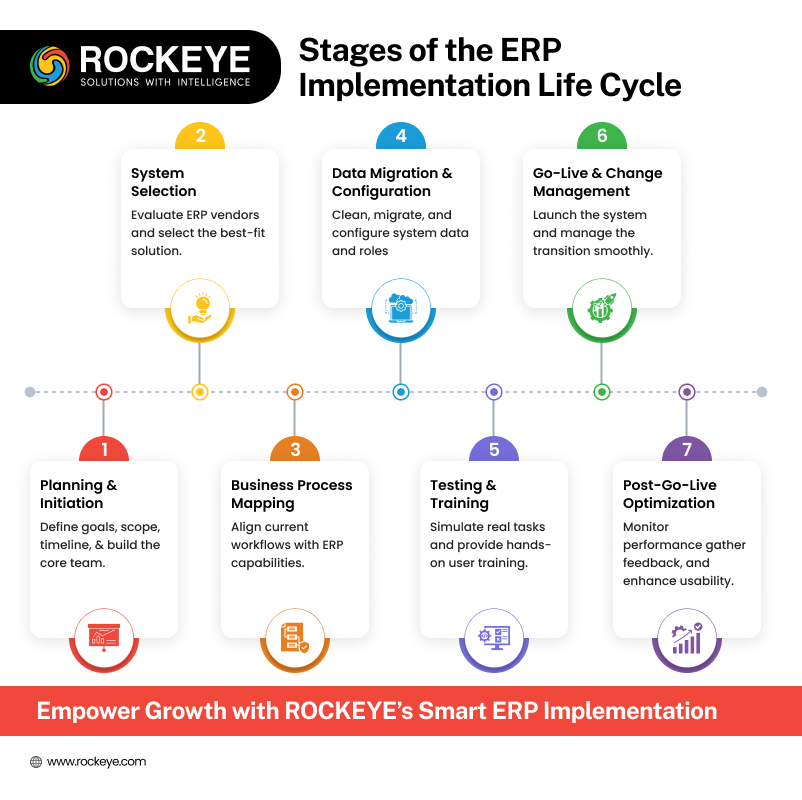
Let us walk through each stage of the life cycle in detail.
1. Planning And Initiation
Every good ERP project starts with planning. This phase sets the tone for the entire implementation. You identify your business goals. Understand what problems the ERP should solve. This phase includes defining the scope and budget. You build a project team. Usually, this includes internal leaders and IT experts.
Stakeholder input is crucial. Everyone who will use the system should be involved early. This helps reduce resistance later.
Here’s what this stage includes:
- Conducting a needs analysis
- Defining clear goals and objectives
- Setting a realistic timeline and budget
- Assembling the core ERP team
- Choosing an implementation partner
2. System Selection
It is critical to pick the right ERP system for your business. You have to check that the system should cater to your business needs and align with certain processes. Here, you have to explore different vendors for ERP software. You have to analyze different elements, like:
- Features
- Scalability level
- Support
- Pricing, etc.
Besides this, you have to pick between the cloud ERP and the on-premises ERP option.
Important steps include:
- Creating a shortlist of vendors
- Requesting demos and RFPs
- Comparing features and integrations
- Assessing vendor support and training offerings
- Checking references and case studies
You have to keep in mind that it is not wise to go for the most popular solution. It is important to pick the one that fits under your budget and helps you achieve your business end goals. You must involve stakeholders during the demo of different software and take their feedback.
3. Business Process Mapping And Gap Analysis
In the next phase, you have to compare your current processes to what the ERP system offers. This is called a gap analysis. You document how things work now. Then, you analyze how the ERP can replicate or improve these processes. You may need to adjust your workflows or customize the ERP.
Key tasks in this stage:
- Mapping core processes like finance, sales, inventory, etc.
- Identifying redundant or inefficient workflows
- Pinpointing gaps between current processes and ERP capabilities
- Deciding what to change and what to customize
You have to try to avoid heavy customization. It can be expensive and make future upgrades harder. Instead, adapt your processes to the ERP when it is possible. This phase ensures smoother data migration and a better user experience later.
4. Data Migration and System Configuration
Your business operations can come to a halt if things go wrong during this step. So, it is important to carry out with proper accuracy. You should start by cleaning your data. It is important to remove the duplicates and fix the errors. Decide what data to keep. You may not need everything from the old system.
Also, system configuration happens here. Your team sets up workflows, user roles, and reporting tools.
Key actions:
- Extracting data from legacy systems
- Cleaning and validating data
- Mapping data to new ERP fields
- Running test migrations
- Configuring modules, access levels, and user dashboards
Don’t rush this stage. You must involve both technical experts and business users. It is crucial to test the system multiple times before you go for the final migration. You have to document every change. A well-configured and clean system leads to accurate reports and smoother operations.
5. Testing And Training
Now, it is time to test the system for real-time events. You have to create test scripts for each department. In which you will simulate tasks, like:
- Creating invoices
- Placing orders
- Running payroll, etc.
It is best to involve real users to get feedback. You have to look for bugs or gaps in functionality and adjust the system as needed.
Then, train your employees according to the feedback. Try to focus on practical tasks rather than just sticking to theory. You have to customize the training to job roles.
Essential actions include:
- Performing unit, system, and integration testing
- Creating a test environment
- Recording bugs and fixing them
- Building role-specific training materials
- Offering hands-on sessions and workshops
You have to keep in mind that proper training will reduce the resistance level and boost confidence. You have to prepare user manuals or video tutorials. This is the phase where people will become comfortable with the new ERP system, which will further lead to a smooth launch.
6. Go-Live And Change Management
When you go live, it means you are running ERP as the main system. So, it is critical to conduct proper planning for the transition.
There are two approaches, namely:
- Phased: In this approach, all the departments in our company will go live one after the other.
- Big bang: Here, everything goes live in one go
Another important aspect is change management, which allows the users to adapt to the systems. So, all the leaders should communicate clearly and offer proper support in the early days. Tasks at this stage:
- Final data migration
- Switching off legacy systems
- Monitoring the new system’s performance
- Offering live support and help desks
- Managing employee feedback
You can expect some hiccups in the process, so it is best to log all the issues. You have to try to resolve them quickly to keep morale high. Let users know they’re not alone.
The success of this stage defines how well the ERP is accepted. Don’t declare victory too early. Keep supporting users and gathering feedback.
7. Post-Go-Live Optimization And Support
Once the dust settles, focus on optimization. Now, you can fine-tune the system based on real-world usage.
You have to monitor KPIs like system uptime, transaction speed, or user adoption and collect feedback regularly. Also, you have to offer ongoing training for new features or hires.
Key actions:
- Monitoring performance and user activity
- Addressing issues quickly
- Reviewing customizations and integrations
- Rolling out updates and patches
- Analyzing ROI
You should also plan for future improvements. ERP systems evolve. Stay updated with new features. Involve users in feedback sessions.
The post-go-live phase isn’t the end. It’s where real value is realized. Continuous improvement turns your ERP from a tool into a competitive advantage.
Also Read:- Understanding ERP Systems
Common Challenges In The ERP Implementation Life Cycle
Despite planning, challenges still appear. Here are some to watch for:
- Poor planning or goal setting
- Lack of user involvement or training
- Data issues like duplicates or missing fields
- Too much customization
- Weak change management
- Underestimating costs or timelines
Recognize these early. Address them with clear communication, expert support, and realistic timelines.
Final Thoughts
Implementing ERP is a major investment. It touches every part of the organization, which makes the understanding of the ERP Implementation Life Cycle highly important. From planning to post-go-live, each stage matters. Each step builds on the last. Skip one, and the results may suffer.
With the right team, tools, and training, your ERP system can transform your business. ROCKEYE has a solid team that can handle the ERP implementation process easily. Contact them today to get all the details.

FAQs
1. How long does a typical ERP implementation life cycle take?
The time will depend on several factors, like:
- Company size,
- Customization needs
- Complexity of the current processes, etc.
Typically, the time ranges between 6 and 18 months.
2. What’s the biggest mistake companies make during ERP implementation?
Lack of proper planning and user training are the biggest mistakes. Many companies skip these steps in the early stages, which further leads to poor adoption of the ERP system. This can delay several projects in the future.
3. Is customization always necessary in ERP systems?
Not always. There are many systems that cover the core functions. You have to go for customizations when they add value to your brand.
4. Can small businesses benefit from ERP systems?
Yes. There are many cloud-based ERPs that are scalable and affordable. They allow small businesses to automate tasks and grow to new heights.
5. What is change management in ERP implementation?
It involves preparing employees for the transition. This includes:
- Communication
- Training,
- Addressing resistance to the new system

